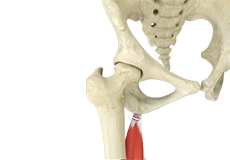
Hamstring Injuries
Hamstring injuries occur when these muscles are strained or pulled. They are common in dancers and athletes of all sorts including runners and those who play football, soccer, basketball, tennis, etc.
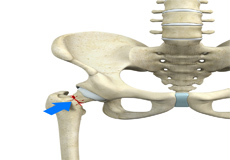
Femoral Neck Fracture
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint made up of the head of the thigh bone or femur that acts as the ball and fits into the rounded socket of the hip bone or acetabulum. The neck of the femur is the region just below the ball of the hip joint.
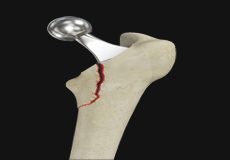
Femur Fracture
The femur or thigh bone is the longest and strongest bone in the body, connecting the hip to the knee. A femur fracture is a break in the femur. The distal femur is the lower part of the thigh bone which flares out like an upside-down funnel and its lower end is covered by a smooth, slippery articular cartilage that protects and cushions the bone during movement. Fracture of the distal femur may involve the cartilaginous surface of the knee as well and result in arthritis.
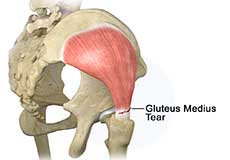
Gluteus Tendon Tear
The gluteal muscles (situated in the buttocks) are necessary for the stability and movement of the hip joints. The tendons of two gluteal muscles (gluteus medius and gluteal minimus) are attached at the outer hip region and are often called the “rotator cuff of the hip.” These tendons may be subject to injury or tearing due to various reasons. Since these gluteal muscles are involved in abduction (movement of your leg away from the midline of the body), the tears are also called abductor tendon tears.
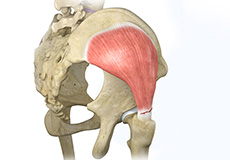
Hip Abductor Tears
Hip abductors are a major group of muscles found in the buttocks. It includes the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fascia lata muscles.
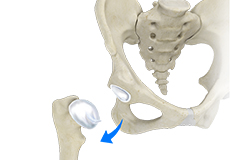
Hip Dislocation
The hip joint is a “ball and socket” joint. The “ball” is the head of the femur or thighbone, and the “socket” is the cup-shaped acetabulum.
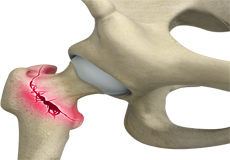
Hip Fracture
The hip joint is a “ball and socket” joint. The “ball” is the head of the femur or thighbone, and the “socket” is the cup-shaped acetabulum. The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain-free movement in the joint.
Hip Injury
The hip joint is one of the most important and flexible joints in the human body which allows us to walk, run, bend and perform physical activities.
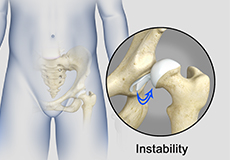
Hip Instability
Injury or damage to these structures can lead to a condition called hip instability when the joint becomes unstable.
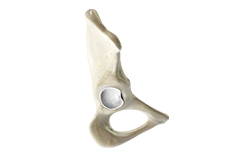
Hip Labral Tear
A hip labral tear is an injury to the labrum, the cartilage that surrounds the outside rim of your hip joint socket.
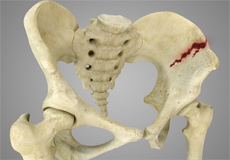
Pelvic Fractures
A pelvic fracture is a condition that occurs due to the breakage of the pelvic bone. It may cause damage to the internal organs, nerves and blood vessels associated with the pelvic region.
Stress Fractures of the Hip
Stress fractures of the hip are a break in the upper part of the thigh bone (femur) that fits into the socket of the hip joint. It can occur in any part of the hip, however, it mostly occurs just below the ball of the ball-and-socket hip joint called the femoral neck.
Subtrochanteric Hip Fracture
A hip fracture is a break that occurs near the hip in the upper part of the femur or thighbone. The thighbone has two bony processes on the upper part - the greater and lesser trochanters. The lesser trochanter projects from the base of the femoral neck on the back of the thighbone. Hip fractures can occur either due to a break in the femoral neck, in the area between the greater and lesser trochanter or below the lesser trochanter.
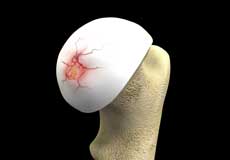
Hip Cartilage Repair
Hip cartilage is a white, tough, flexible tissue covering the ball (femoral head) and socket (acetabulum) of your hip joint. It acts as a cushion or shock-absorber and allows the bones to slide over one another by providing a smooth surface in the joint.
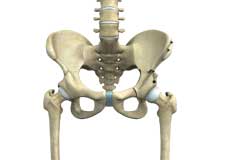
Hip Preservation Surgery
The hip is a ball and socket joint comprising of the femur (thigh bone) and the pelvic bone. The head of the femur (ball) articulates with a cavity (socket) called the acetabulum in the pelvic bone. To facilitate the smooth and frictionless movement of the hip joint, the articulating surfaces of the femur head and acetabulum are covered by spongy articular cartilage.

Hip Labral Repair
Labrum is a ring of strong fibrocartilaginous tissue lining around the socket of the hip joint. Labrum serves many functions where it acts as a shock absorber, lubricates the joint, and distributes the pressure equally. It holds the head of the femur in place and prevents the lateral and vertical movement of the femur head within the joint. It also deepens the acetabular cavity and offers stability against femoral head translation.
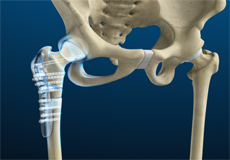
Hip Fracture Surgery
Hip fractures involve a break that occurs near the hip in the upper part of the femur or thigh bone. The thigh bone has two bony processes on the upper part - the greater and lesser trochanters. The lesser trochanter projects from the base of the femoral neck on the back of the thigh bone. Hip fractures can occur either due to a break in the femoral neck, in the area between the greater and lesser trochanter or below the lesser trochanter.
Physical Therapy for Hip
Physical therapy is an exercise program that helps you to improve movement, relieve pain, encourage blood flow for faster healing, and restore your physical function and fitness level.
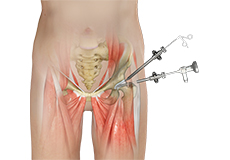
Hip Arthroscopy
Hip arthroscopy, also referred to as keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, is a procedure in which an arthroscope is inserted into your hip joint to check for any damage and repair it simultaneously.
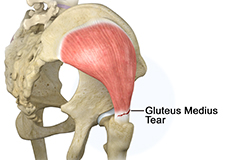
Gluteus Medius Tear
A gluteus medius tear is the partial or complete rupture of the gluteus medius muscle due to severe muscle strain.
Hip Reconstruction
Hip reconstruction is a surgery to repair or replace a damaged hip joint that causes pain and limits your movement.
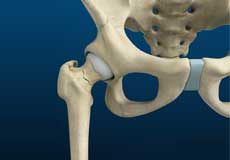
Hip Joint
The hip joint is the largest weight-bearing joint in the human body. It is also referred to as a ball and socket joint and is surrounded by muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The thigh bone or femur and the pelvis join to form the hip joint.
Any injury or disease of the hip will adversely affect the joint's range of motion and ability to bear weight.
The hip joint is made up of the following:
- Bones and joints
- Ligaments of the joint capsule
- Muscles and tendons
- Nerves and blood vessels that supply the bones and muscles of the hip
Bones and Joints
The hip joint is the junction where the hip joins the leg to the trunk of the body. It is comprised of two bones: the thigh bone or femur and the pelvis which is made up of three bones called ilium, ischium, and pubis. The ball of the hip joint is made by the femoral head while the socket is formed by the acetabulum. The Acetabulum is a deep, circular socket formed on the outer edge of the pelvis by the union of three bones: ilium, ischium, and pubis. The lower part of the ilium is attached by the pubis while the ischium is considerably behind the pubis. The stability of the hip is provided by the joint capsule or acetabulum and the muscles and ligaments which surround and support the hip joint.
The head of the femur rotates and glides within the acetabulum. A fibrocartilagenous lining called the labrum is attached to the acetabulum and further increases the depth of the socket.
The femur or thigh bone is one of the longest bones in the human body. The upper part of the thigh bone consists of the femoral head, femoral neck, and greater and lesser trochanters. The head of the femur joins the pelvis (acetabulum) to form the hip joint. Next, to the femoral neck, there are two protrusions known as greater and lesser trochanters which serve as sites of muscle attachment.
Articular cartilage is the thin, tough, flexible, and slippery surface lubricated by synovial fluid that covers the weight-bearing bones of the body. It enables smooth movements of the bones and reduces friction.
Ligaments
Ligaments are fibrous structures that connect bones to other bones. The hip joint is encircled with ligaments to provide stability to the hip by forming a dense and fibrous structure around the joint capsule. The ligaments adjoining the hip joint include:
- Iliofemoral ligament: This is a Y-shaped ligament that connects the pelvis to the femoral head at the front of the joint. It helps in limiting the over-extension of the hip.
- Pubofemoral ligament: This is a triangular shaped ligament that extends between the upper portion of the pubis and the iliofemoral ligament. It attaches the pubis to the femoral head.
- Ischiofemoral ligament: This is a group of strong fibers that arise from the ischium behind the acetabulum and merge with the fibers of the joint capsule.
- Ligamentum teres: This is a small ligament that extends from the tip of the femoral head to the acetabulum. Although it has no role in hip movement, it does have a small artery within that supplies blood to a part of the femoral head.
- Acetabular labrum: The labrum is a fibrous cartilage ring which lines the acetabular socket. It deepens the cavity, increasing the stability and strength of the hip joint.
Muscles and Tendons
A long tendon called the iliotibial band runs along the femur from the hip to the knee and serves as an attachment site for several hip muscles including the following:
- Gluteals: These are the muscles that form the buttocks. There are three muscles (gluteus minimus, gluteus maximus, and gluteus medius) that attach to the back of the pelvis and insert into the greater trochanter of the femur.
- Adductors: These muscles are located in the thigh which helps in adduction, the action of pulling the leg back towards the midline.
- Iliopsoas: This muscle is located in front of the hip joint and provides flexion. It is a deep muscle that originates from the lower back and pelvis and extends up to the inside surface of the upper part of the femur.
- Rectus femoris: This is the largest band of muscles located in front of the thigh. They also are hip flexors.
- Hamstring muscles: These begin at the bottom of the pelvis and run down the back of the thigh. Because they cross the back of the hip joint, they help in extension of the hip by pulling it backward.
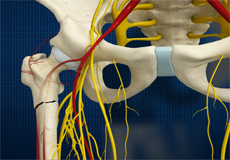
Nerves and Arteries
Nerves of the hip transfer signals from the brain to the muscles to aid in hip movement. They also carry the sensory signals such as touch, pain, and temperature back to the brain.
The main nerves in the hip region include the femoral nerve in the front of the femur and the sciatic nerve at the back. The hip is also supplied by a smaller nerve known as the obturator nerve.
In addition to these nerves, there are blood vessels that supply blood to the lower limbs. The femoral artery, one of the largest arteries in the body, arises deep in the pelvis and can be felt in front of the upper thigh.
Hip Movements
All of the anatomical parts of the hip work together to enable various hip movements. Hip movements include flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction, and hip rotation.
